News
Anti-cancer pioneers: apoptosis induction in breast cancer cells by L selenium-methyl selenocysteine
2024-11-18 10:11:02
Hits:0
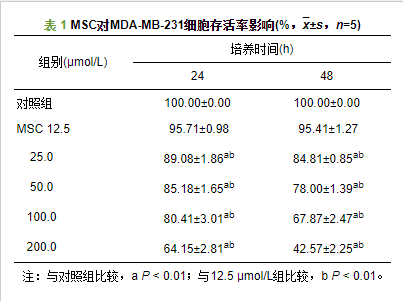
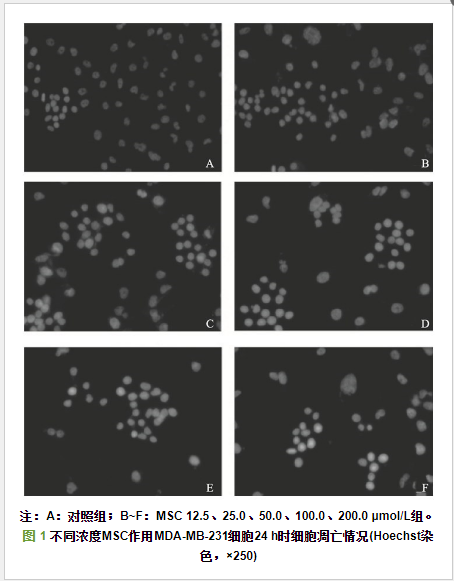
MSC对MDA-MB-231细胞凋亡影响
MSC对MDA-MB-231细胞SOD、GSH-Px活力、MDA水平影响
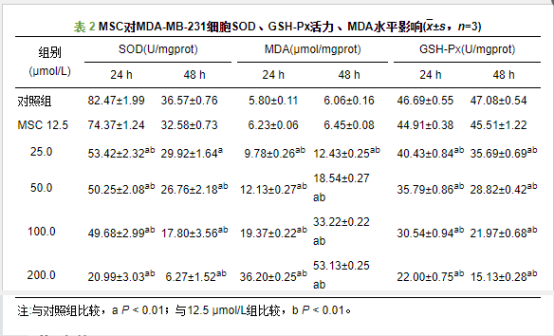
The research results indicate that MSC can reduce the activity of SOD and GSH-Px in MDA-MB-231 cells while increasing MDA levels, showing a dose- and time-dependent effect. This suggests that MSC induces oxidative stress in MDA-MB-231 cells by decreasing intracellular SOD and GSH-Px activities and increasing MDA levels, leading to oxidative damage and subsequent cell apoptosis. This finding is consistent with existing research on oxidative stress regulation mechanisms in tumor cell apoptosis.
参考:袁国海, 黄秋, 邵继红, 罗雅婕, 谢蒙蒙. 硒-甲基硒代半胱氨酸诱导乳腺癌细胞凋亡作用. 中国公共卫生, 2016, 32(9): 1183-1185.